We’re only halfway through 2017, but the world has already seen at least 2 global ransomware attacks. According to a report by Kaspersky, ransomware attacks have increased by 11.4% in the past 12 months, to almost 2.6 million worldwide. The complete extent of each attack remains unknown yet, but cybercriminals have succeeded in locking out organizations as well as individuals from their systems and data. In the case of the more recent Petya ransomware attack, people are unable to retrieve their data even after making ransom payouts.
Disabling access to sensitive data on computers and mobile devices not only causes inconvenience to end users, but can disrupt essential business processes and operations of enterprises, both large and small. Individuals, businesses, government agencies, educational institutions – ransomware affects everyone.
Both Petya and WannaCry exploit the EternalBlue vulnerability in Microsoft Windows to infect their victims’ systems. The zero-day exploit, purportedly created by the NSA, is one of the tools leaked online in April by hacker group Shadow Brokers. Hackers tweaked the tool to add a few more features to evade detection, spread and replicate rapidly, and infect more systems, before unleashing them across the world.
Growing ransomware and other cyberthreats make it challenging for organizations to undertake and expand their digital transformation efforts. While automation through IT increases overall efficiency, it also leaves organizations more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Existing cybersecurity solutions cannot keep up with the increasing complexity and sophistication of cybercriminals and latest cyberthreats, which makes matters worse for enterprises.
Strong firewalls, antivirus solutions, regular updating and patching of enterprise software and systems offer temporary relief for organizations, but if not undertaken regularly, create more vulnerabilities in the corporate network they are supposed to protect. It is time for businesses to refresh their cybersecurity perspectives and look for ways to protect their critical assets not just from current threats, but also tomorrow’s cyberthreats.
Blockchain could be the answer for future-proofing enterprises’ cybersecurity measures. Both Petya and WannaCry ransomware attacks exploited an old, unpatched vulnerability in Microsoft Windows. Legacy hardware in the enterprise, inadequate IT policies, infrequent patching of software can leave corporate networks vulnerable to attacks, despite heavy investment in the latest cybersecurity solutions available in the market.
A blockchain-enabled cybersecurity solution, on the other hand, offers enterprises a way to protect even their legacy and outdated IT systems. The decentralized nature of the distributed ledger technology prevents enterprises from having a single point of failure from where an infection can enter the network and lock down critical infrastructure.
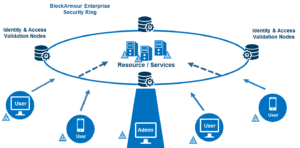
Creating a virtual ring fence, or a Blockchain-Defined Perimeter (BDP) around an organization’s most critical infrastructure using blockchain and TLS technology renders enterprise systems invisible to hackers. What cybercriminals cannot see, they cannot attack – keeping data and assets safe from ransomware attacks. In addition, a blockchain-based cybersecurity solution also encrypts the data stored and transferred within the network, and can be used to implement stronger and more secure identity and access management.
A BDP solution will allow organizations to enforce tighter access controls and prevent mishandling of data by unauthorized users. When access to sensitive data gets controlled more effectively, the threat of ransomware correspondingly becomes more controlled and manageable. Cybercriminals targeting enterprises can no longer gain unauthorized access into a blockchain-enhanced infrastructure within the enterprise networks. Moreover, encryption of the data ensures additional security, rendering any data, if accessed, unusable.
Data stored in a blockchain undergoes sequential hashing to generate a unique fingerprint. Any transaction of data taking place within a blockchain causes the creation of another block which gets added to the chain to ensure data integrity. Data stored in the blockchain is immutable – any attempt to access or alter data stored in a blockchain is indelibly recorded, empowering enterprises to protect their data from the risk of insider threats well.
Blockchain is one of the key reasons for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to become a popular and trusted way to transact worldwide. While most blockchain applications are currently focused in the fintech space, newer use cases are emerging outside this space to explore the use of blockchain. Cybersecurity is one such important area for exploring the use of blockchain technology.
It is time we look towards this technology to solve the rising challenges of cybersecurity across industries worldwide.
[su_box title=”About Floyd DCosta” style=”noise” box_color=”#336588″][short_info id=’102714′ desc=”true” all=”false”][/su_box]






