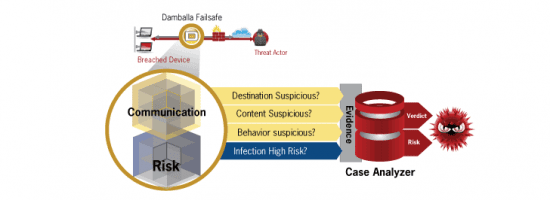
While malware developers keep working on improving their creations by leveraging non-HTTP channels, such as peer-to-peer, most malicious programs still use HTTP. Worryingly, over 75% of these pieces of malware are capable of evading traditional security measures, researchers from Damballa warn.
“Malware today is using HTTP to ‘blend in’ and evade detection by sending small traces of information over the core ports and protocols that enterprises allow in and out of their network. Our research indicates that firewalls and IPS are highly ineffective at detecting next-gen malware infected devices,” Damballa researcher Terry Nelms noted.
In his research, Nelms utilized a prototype tool called ExecScent to identify malware on hundreds of hosts running traditional security products.
SOURCE: news.softpedia.com
The opinions expressed in this post belongs to the individual contributors and do not necessarily reflect the views of Information Security Buzz.