Thinking of migrating your On-premise Email to the IT cloud? you should know your risks!
Research conducted by Gartner and published by multiple sources suggests that the number of Cloud based email users is on the rise—from 12% in 2013, to an anticipated 50% by 2022. While this shift to the IT Cloud brings many benefits, it also leaves the organization with a new set of security challenges.
Many of these challenges relate to the lack of organizational understanding pertaining to the Shared Responsibility model prevalent in the IT Cloud. The model states that the vendor is responsible for creating a secured service, and the client is accountable for using the service in a secure manner. A simple example is Multi Factor Authentication, which most IT Cloud services offer but only a few organizations utilize.
The perceived risk for organizations moving to the IT Cloud is low compared to the actual risk it entails. This is mainly due to a false sense of belief that Cloud vendors handle security end-to-end.
One specific case, where the responsibility to secure falls entirely on the organization’s shoulders is the use of third party applications connecting to IT Cloud email. This scenario did not exist with on-premise systems and falls between the cracks with the shift to IT Cloud. In this new era, employees have the ability to grant applications access to their corporate information. However, organizations do not have the capability to monitor, let alone prevent it. This creates a new security paradigm which gives employees privileges that in the past could only be performed by IT personnel having the authority with on-premise systems.
Third party applications: The Give it All Up Attitude
IT Cloud email platforms have created comprehensive sets of APIs to allow third party integrations, offering organizations almost limitless ways to interact with their data. However, these APIs conceal a substantial risk that most organizations do not take into account.
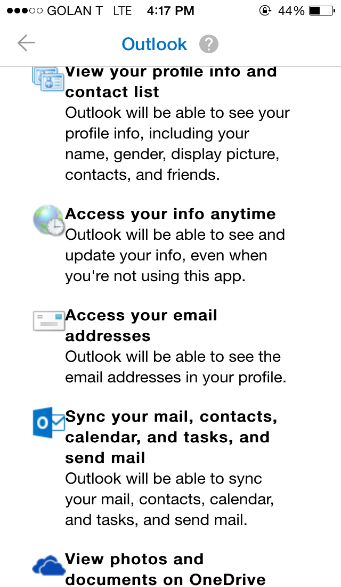
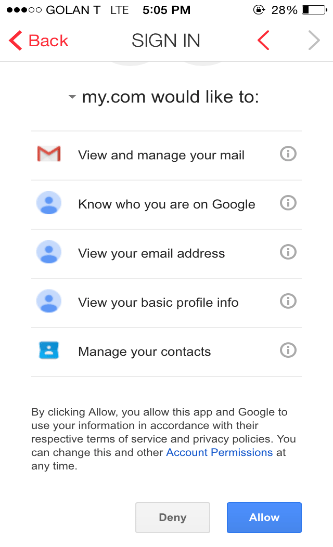
We’ve all seen this screen before and have gotten used to pressing “yes” without thinking twice, let alone reading and understanding the full implications of that simple little click. This attitude of relinquishing access to our information has become the norm, as it is requested by almost every App we install on our phones, as well as every time we sign up to a service using Google login.
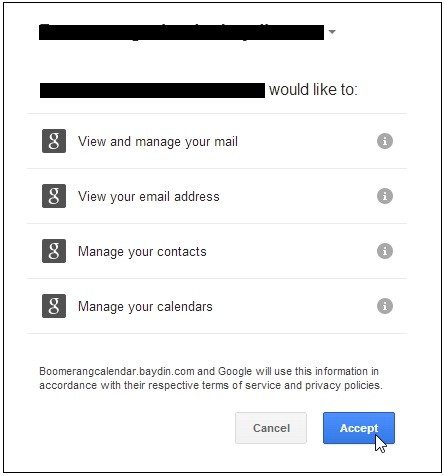
With the move of organizations to IT Cloud email, the approach of users to easily give access to their information suddenly becomes an organizational nightmare. From a security standpoint this attitude involves repercussions, eroding years of costly investment in employee security awareness.
Warning: You’ve Got Mail
Email App companies are in a constant battle to serve an experience that is on par, or exceeds the native one (i.e. Gmail App that works only with Google services). This is a rigorous task when taking into account that IT Cloud email providers do not extend some of their functionality to third party Apps, such as push notifications on incoming emails. In order to mimic this experience, App makers continuously poll the Cloud email service to know when a new message is waiting.
This creates a few challenges for the App makers, the main one being that constant polling directly from the device, impacts battery life. The App companies found a workaround by moving the activity to their backend servers and pushing the message to the device using their proprietary technologies. Essentially, this creates a tunnel where all user information (i.e. email, calendar, contacts etc.) is redirected through the App’s servers, potentially storing it for an undetermined period of time. Although an elegant solution for the App companies, this creates a substantial security risk for organizations. In fact, Email Apps can be a critical danger to an organization.
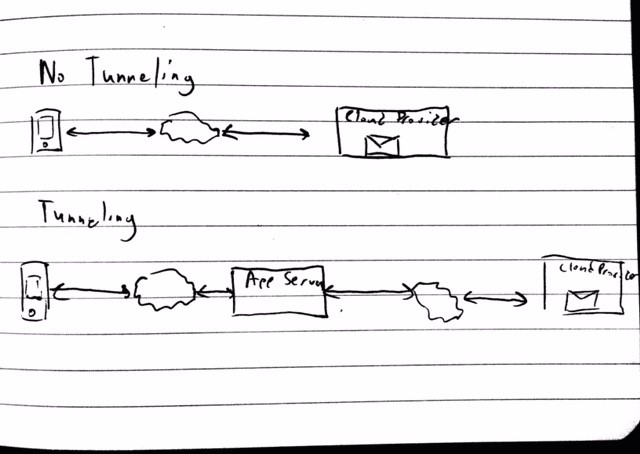
Compared to service providers such as Google or Microsoft, App companies have limited resources for securing their services. This opens a much simpler way of attacking an organization’s email as compared to compromising Google itself. Last years Sony email attack is a prime example of the type of valuable data corporate email can contain, and just how detrimental malicious access can be for an organization.
Why should you care? Your organization just spent months debating over email security, reviewing the T&C, and Privacy Policy, to create a secure transition to the cloud — Only to find out that your employee granted access to a random company to tunnel his credentials, emails, calendars, and contacts. Not the ideal scenario especially when Office 365 and Google Apps lack the built-in functionality to block this type of access.
Putting it to the Test
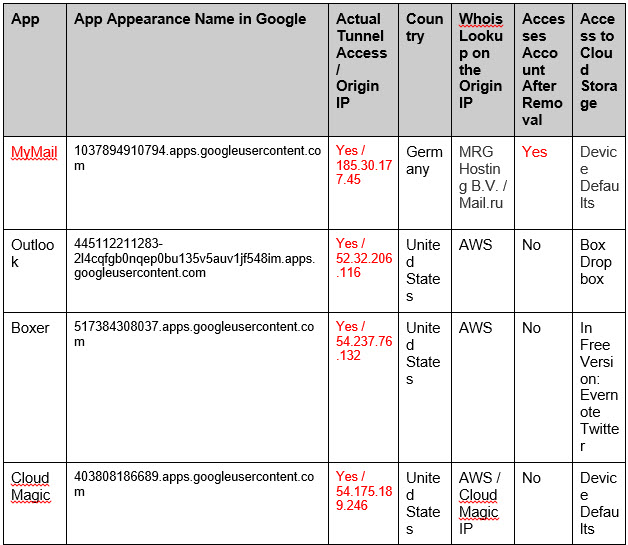
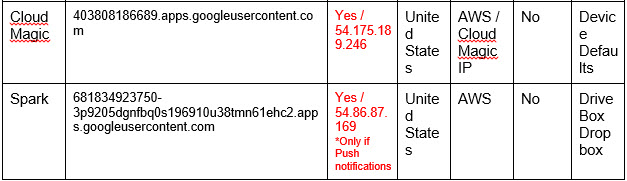
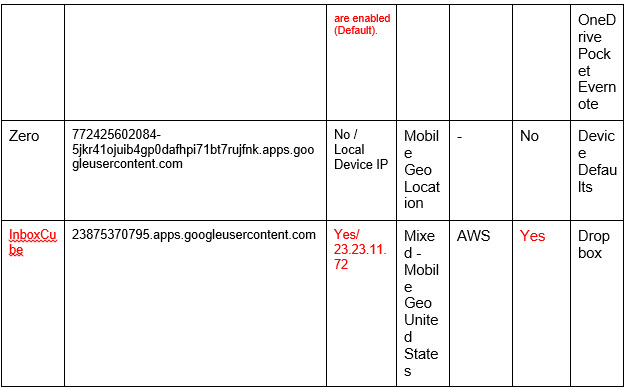
Examining a few of the most common email Apps on the market today helps to paint a clearer picture of what it means to allow access to third party apps. We examined Boxer, Microsoft Outlook (previously Acompli), Spark, CloudMagic, MyMail, Zero, and InboxCube. Our test consisted of reviewing the Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, access rights, file sharing capabilities, deletion process, and lastly the actual connections to the Cloud email provider and their origins.
Terms and Conditions Do Apply
The Apps are split into two groups: those with policies that allow for them to tunnel data through independent servers, and those which do not. From our observation, all of the Apps belong to the first group, except for Zero which is in the latter. When overviewing the “legal” aspects, both the Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policies grant the App companies the rights for this type of data usage. Excerpts from the Privacy Policies of the tunneling group are as follows:
- Microsoft Outlook:
“we may access, disclose and preserve your personal information, including your private content (such as the content of your emails, other private communications or files in private folders), when we have a good faith belief that doing so is necessary”
- Boxer:
״When you log into your email account in Boxer, you are granting Boxer permission to securely access your information contained in or associated with those accounts.”
- CloudMagic:
“We then use the authorization provided to download your emails on the cloud and push to your devices. We use AWS servers to store your data: emails and authorization.”
In contrast, Zero’s Privacy Policy should be positively noted. The service specifically states that they do not store any data, and or credentials on their servers:“Zero App DOES NOT STORE your messages, contacts or private information on our or any third party servers. Your email messages, your account password and all other personal information that you share with others when using Zero, STAY ON YOUR PHONE or with your email provider.”
Authentication
The Apps state that they use OAuth tokens when possible, and do not store credentials on their servers in that scenario. However, if the email provider or App maker does not support OAuth they will store credentials in order to support their service. This practice is so problematic that the EU parliament IT department ordered staff to remove the app and reset their passwords in wake of the Outlook app siphoning user credentials.
While the use of OAuth tokens is considered good practice, it heavily depends on the implementation. In cases where the device is lost or compromised, the token itself might be enough to hijack the authenticated session. Therefor, granting attackers access to account information like we have previously seen in the OAuth Yammer flaw.
Deleting “Email Apps” – Keep your Fingers Crossed
Email Apps specifically state they store credentials and data when needed to provide service. There is no guarantee that App companies will completely remove the credentials when users terminate that service. In fact, all the information is stored on external servers, and the user has no way to confirm credential and data deletion. In scenarios where App companies execute data replication (ie. BI Analysis, snapshots, and backups), data deletion becomes even more complex and might not happen altogether.
Testing was conducted to identify whether Apps continue to poll the Cloud email provider subsequent to user account removal. From the Apps surveyed both MyMail and InboxCube showed this type of activity. In order to fully address this issue, users need to manually revoke the OAuth token or change their password depending on the implemented authentication scheme. Both of these task are cumbersome from an administrative standpoint and are almost impossible without automation. Furthermore, organizations should continually monitor Cloud email for unauthorized OAuth grants and ASP’s (Application Specific Password); guaranteeing that only whitelisted Apps meeting company policy have access to employee data.
Sharing isn’t Necessarily Caring
Organizations implement numerous technologies (ie. USB Blocking, DLP, etc.) that limit employees ability to leak unauthorized data off-premise. The moment data leaves the controlled environment, organizations have limited ability to know who is accessing it, and where it is being used. Email has always been one of the harder challenges to address in this space since users frequently send authorized attachments off-premise, limiting the ability to block this type of behavior.
Email Apps add another layer on top of this. Not only do they hold mass amounts of sensitive data, most of them have built-in file share capabilities. Integration with cloud storage solutions such as Google Drive, Box, OneDrive, Evernote are very popular, 4 out of the 7 Apps examined had these built-in features. These capabilities enable the user to save an attachment directly to a Cloud drive, which isn’t necessarily connected to same organizational account.
There is one main difference when comparing Apps that have built-in sharing capabilities to those that use native OS sharing. When using native OS sharing, organizations have multiple solutions to control share settings using simple device policies. Where as with the third party Apps the capability is housed inside the App limiting the control. This is just another example where the use of Cloud technologies becomes an ever increasing threat to manage for organizations.
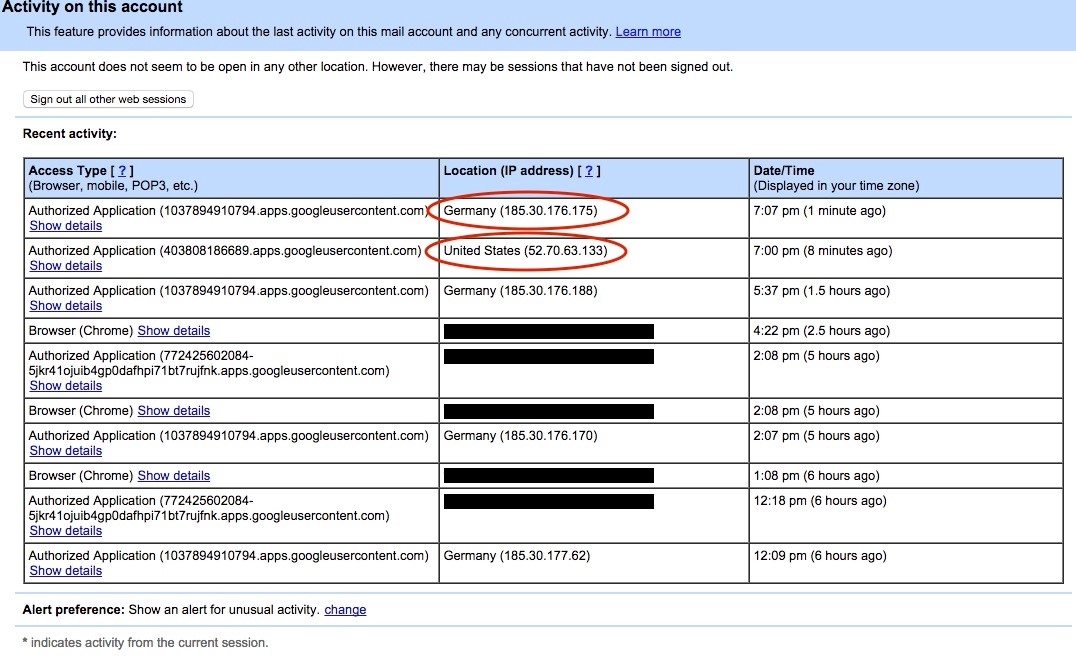
End user view of Google activity page showing access from tunnel IP Addresses:
 [su_box title=”About FireLayers” style=”noise” box_color=”#336588″]
[su_box title=”About FireLayers” style=”noise” box_color=”#336588″] FireLayers enables companies to adopt the cloud responsibly, while ensuring security, compliance and governance of any cloud application on any device by any user. The FireLayers Cloud Application Security Gateway, our inaugural solution, is the industry’s first to leverage XACML-based granular policies to deliver full control over popular apps like Salesforce, Office365, SuccessFactors, NetSuite and endless others as well as customized and homegrown cloud applications. With our cloud application security gateway, enterprises gain new levels of security, visibility and control across their cloud application landscape.[/su_box]
FireLayers enables companies to adopt the cloud responsibly, while ensuring security, compliance and governance of any cloud application on any device by any user. The FireLayers Cloud Application Security Gateway, our inaugural solution, is the industry’s first to leverage XACML-based granular policies to deliver full control over popular apps like Salesforce, Office365, SuccessFactors, NetSuite and endless others as well as customized and homegrown cloud applications. With our cloud application security gateway, enterprises gain new levels of security, visibility and control across their cloud application landscape.[/su_box]
The opinions expressed in this post belongs to the individual contributors and do not necessarily reflect the views of Information Security Buzz.



