Cybercriminals use Microsoft OneNote attachments in phishing emails to spread malware and password stealers. Phishing campaigns are one of the most typical ways criminals obtain private or sensitive information. According to Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, 94% of the malware is delivered by email.
Malicious Word and Excel attachments for phishing have been prevalent for a long time, known to compromise recipients using macros to download and install malware. However, in July 2022, Microsoft blocked Macros by default on all Office applications, making this approach unreliable for spreading malware. Since then, hackers have come up with various modern email-based initial access vectors that include using .iso and .zip container files to deliver malicious payloads, forcing Microsoft to fix identified bugs that allowed ISOs to bypass security warnings.
The RAT in mi Note
Cybercriminals are known to be innovative when trying to find novel ways to spread malware. Recently, security researchers came across multiple spam emails containing an unusual file type for an email attachment: a Microsoft OneNote file (.one). Analyzing the spam email content, they use typical social engineering tactics like invoice notifications and known brands such as “DHL” to lure their victims.
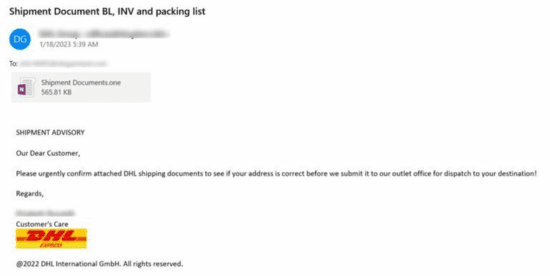
As Microsoft OneNote is installed by default in all Microsoft 365 or desktop Office installations, even if a Windows user does not use the application, it is still available to open the file format. Upon opening the OneNote file attachment, it will display a “CLICK TO VIEW DOCUMENT” button. Once the victim clicks this, there will be a pop-up warning about opening attachments that could harm the computer. Some users may ignore this warning, and the execution of the suspicious file proceeds.
Unlike Word and Excel, OneNote does not support macros. Instead, OneNote allows users to insert attachments into a NoteBook. To launch the attachments, users are required to double-click on them. Threat actors are abusing this feature by attaching malicious Virtual Basic Script attachments that automatically launch the script when double-clicked to download malware from a remote site and install it.
The researchers found that the embedded executable files are hidden in the OneNote file. These executable files are hidden behind the normal image “CLICK TO VIEW DOCUMENT” that the cyber criminals made to look like a button.
When launching the OneNote attachments, individuals will get a warning that doing so can harm their computer and data. Unfortunately, history has taught us that these types of prompts are commonly ignored, and users click the OK button.
Clicking the OK button will launch the VBS script to connect to a remote server, download and install malware. The malicious payload is verified to be AsyncRAT, a type of Remote Access Trojan (RAT). It is an open-source tool created to control other computers remotely. Once successfully installed, AsyncRAT can perform the following:
- Keylogging
- Recording of the screen
- Downloading or uploading additional malware
What Am I Gonna Do?
Once installed, this type of malware allows threat actors to remotely access a victim’s device to steal files or passwords stored in browsers, take screenshots, and sometimes even record video using webcams. Threat actors also commonly use remote access trojans to steal cryptocurrency wallets from victims’ devices, making this a costly infection.
Microsoft has already halted cryptocurrency mining on its platform, which has often been linked to unauthorized account access. This has significantly reduced cloud service degradation and disruption.
However, to adequately protect themselves, it is vital for OneNote users not to disregard warnings by the application. In fact, more generally they should:
- Avoid opening attachments from unknown or untrusted sources
- Be cautious of ‘unexpected’ attachments
- Take steps to verify the sender’s identity
From an organisational perspective, basic security measures should include:
- Employee education. Regularly educate your employees on the dangers of phishing attacks and the importance of being cautious when handling emails and attachments. This will help prevent human error, which is a common cause of successful phishing attacks.
- Use multifactor authentication. Implementing multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security and makes it more difficult for cybercriminals to make use of stolen credentials and ultimately gain access to sensitive information.
- Make sure all end points have up to date anti-virus software. This will help detect and prevent malicious attachments from infecting computers
The opinions expressed in this post belongs to the individual contributors and do not necessarily reflect the views of Information Security Buzz.



